Photography Sage
Your guide to capturing moments and mastering photography skills.
Cardio: The Love-Hate Relationship You Can't Escape
Discover the rollercoaster of cardio love and hate! Join us as we explore why this workout is both a must and a challenge. Dive in now!
The Benefits of Cardio: Why You Can't Ignore This Love-Hate Relationship
Cardiovascular exercise, commonly known as cardio, is often met with mixed feelings by fitness enthusiasts. However, its myriad benefits cannot be understated. Engaging in regular cardio activities, such as running, cycling, or swimming, can significantly improve heart health, enhance lung capacity, and boost overall endurance. According to the American Heart Association, just 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous activity weekly can lower the risk of heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. This essential workout component is not just a means to trim down; it plays a vital role in fortifying your body and mind against various health challenges.
Moreover, the psychological benefits of cardio are equally noteworthy. Engaging in consistent cardiovascular exercise has been linked to improved moods and decreased anxiety levels. The National Institutes of Health highlight that physical activity triggers the production of endorphins, which can lead to a sense of euphoria often referred to as the ‘runner’s high.’ Additionally, incorporating cardio into your routine can enhance your sleep quality, increase energy levels, and sharpen mental focus, creating a love-hate relationship that many cannot ignore. While the workouts might feel daunting at times, the rewards—both physical and mental—are truly worth the effort.
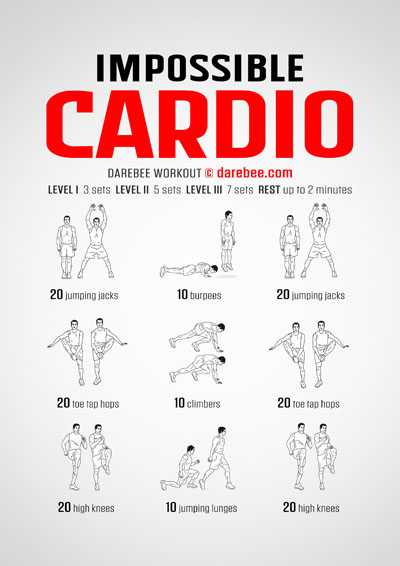
How to Make Cardio Enjoyable: Tips for Embracing the Grind
Making cardio enjoyable can transform your workout routine and help you embrace the grind. One effective approach is to vary your routines to keep things fresh and exciting. Consider incorporating different types of cardio workouts, such as running, cycling, swimming, or group classes, to find what you love most. For additional ideas, check out this informative resource on varied cardio workouts. You can also create a motivational playlist filled with your favorite upbeat songs to boost your mood and energy levels while you exercise.
Another way to enhance your cardio experience is to set specific, achievable goals. Whether it's increasing the distance you can run, improving your cycling speed, or simply completing a certain number of sessions each week, having clear targets can incentivize you to push yourself. To make your cardio sessions even more enticing, consider inviting a friend to join you or participating in community events like fun runs or fitness challenges. This can not only make exercising more social but also keep you accountable. For more tips on setting effective fitness goals, visit Healthline.
Cardio Myths Debunked: What You Need to Know to Love It (or Leave It)
When it comes to cardio, there are numerous myths that can deter you from embracing this essential form of exercise. One of the most common misconceptions is that cardio is the only way to lose weight. While cardiovascular activities like running and cycling can help burn calories, integrating resistance training into your routine is equally important for building muscle and boosting metabolism. According to the National Institutes of Health, a combination of both cardio and strength training is most effective for long-term weight management and overall health.
Another prevalent myth is that you must spend hours doing cardio to see results. In reality, high-intensity interval training (HIIT) can provide an effective cardio workout in a fraction of the time. Studies have shown that just 20-30 minutes of HIIT can significantly improve cardiovascular health and boost calorie burn. Understanding these facts can help you appreciate cardio for its benefits without feeling overwhelmed by the time commitment, allowing you to make informed choices about your fitness routine.